|
Blood Pressure and Stroke
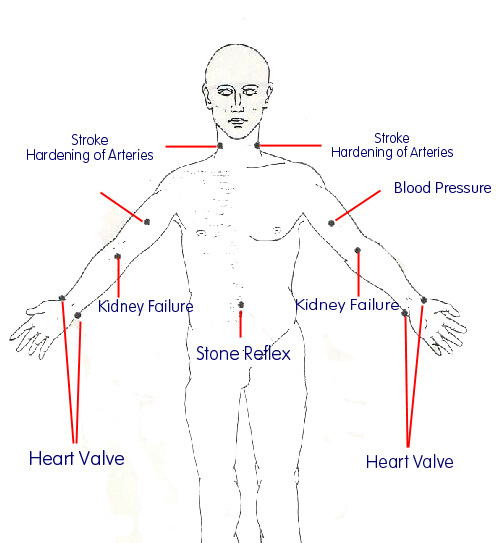
HARDENING OF THE ARTERIES:
( Arteriosclerosis)
A term applied to a number of
pathological conditions in which there is thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries.
This results in altered function of tissues and organs.
Arteriosclerosis (build-up of calcium on the inside of artery walls) and atherosclerosis (deposits of fatty substances) have about the same effect on circulation.
Either condition causes strokes, coronary disease (angina), and high blood pressure.
High blood pressure can also cause arteriosclerosis.
Narrowing of the arteries forces blood pressure that is already high to become even higher. As the arteries become less pliable and less permeable, cell starvation results due to insufficient circulation in the cells.
An individual will suffer a heart attack, also referred to as a myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary occlusion (a coronary), when one of the coronary arteries becomes completely obstructed by accumulated deposits or by a blood clot that has either formed or been snagged on the deposit.
Older people are at greater risk for this kind of heart trouble. When arteriosclerosis occludes the arterial supply of blood to the brain, a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or stroke occurs.
Arteriosclerosis obliterans occurs when the lower limbs are affected, in the early stages, the major arteries that carry blood to the legs and the feet become narrowed by fatty deposits.
Then problems with aching muscles, fatigue, and cramp-like pains in the ankles and legs occur. Depending on which arteries are blocked, the pain may also be in the hips and thighs. Leg pain brought on by walking that is promptly relieved by sitting is called claudication (lameness, limping).
Additional symptoms include numbness, weakness, and a heavy feeling in the legs. These symptoms occur when the arteries are clogged with cholesterol plaque.
Pain is experienced if the amount of oxygenated blood is insufficient to meet the needs of the exercising leg muscles.
|
